
Python exercises
Photo credit xckd.com/189
Exer 1. Ask the user for input, then greet the user. Store the user’s response in a variable and print it out.
Exer 2. Ask the user the year he was born, then print out his age.
Exer 3. Print a triangle of asterisk, see the output below
*
**
***
****
*****
******
*******
********
*********
There are 10 asterisk on the last line of the printed output
Exer 4. Print a triangle of asterisk, just like how you did it in Exer 3, but this time, ask the user how many layers of asterisk he wants to print.
For additional difficulty, you may also ask the user what character to print, use that instead of the asterisk. If the user doesn’t input any character, then use the asterisk
Exer 5. FizzBuzz
Loop through the numbers 1 through 100. If the number is odd, print “Fizz”. If it’s even, print “Buzz”. If the number is a multiple of 10, print “FizzBuzz”
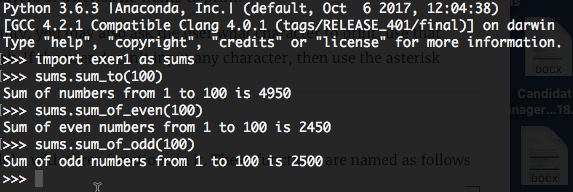
Exer 6 Create a module with three functions in it. These functions are named as follows
sum_to(end)
sum_of_even(end)
sum_of_odd(end)
The module should be loadable from the REPL, sample usage is as follows
You should also be able to run the module as a script, like so
$ python sums.py 100
Sum of numbers from 1 to 100 is 4950
Since there are 3 functions in the module, make the default function to run from __main__ to be “sum_to”. It should be able to read the argument that was passed from the command line.
For this exercise, you need the following skills and knowledge
- loop constructs
- work with functions and parameters
- use of basic math operators, specifically the modulo
- how to work with Python basic types, specifically converting from
strtoint - knowledge of Python execution model, know when a module is run as a script and when it’s loaded from the REPL
Exer 7. Find the divisors of a number.
Create a program that asks the user for a number and then prints out a list of all the divisors of that number. (A divisor is a number that divides evenly into another number. For example, 13 is a divisor of 26 because 26 / 13 has no remainder.)
$ python exer2.py
Enter a number: 10 [enter]
[1,2,5,10]
You don’t have to find an efficient algorithm like constant time, O(1), you can solve it by brute force methods or O(n). You can solve this this way
- Get a number input from the user, convert it to a Number using the int() function, save it to a variable named num
- Generate a range; you may or may not convert it to a list, it doesn’t matter
- Create an empty list
- Go through each item in the range, get the quotient of num and the current item (in the range) — in remainder form, so modulo). If the remainder is == 0, add the current item in the list
- Rinse and repeat, until all the items in the range is processed
Remember that ranges are half-closed, meaning, it will exclude the last item in the range
Exer 8 Greatest Common Factor
Given two non-negative integers firstNum and secondNum, find the greatest common factor. There are many solutions to this problem, but for the purpose of our exercise, we’ll use the Euclidean algorithm. The steps are as follows;
- Find the bigger (bigNum) and smaller (smallNum)
- Get the quotient (in remainder form) of bigNum and smallNum
- If the remainder (rem) is
== 0, then were done, the GCF is smallNum - However, if
rem != 0, then we do the followingbigNum = smallNumsmallNum = rem- Go back to step number 2 (Get the quotient of bigNum and smallNum … )
Pass the numbers as argument to the command line. This module needs to be ran as a script.
This is an exercise on the following areas
- Use of Math operators
- Python loop constructs
- How to use built-in Python modules
- Knowledge of Python data types and basic conversions
- Knowledge of some data structures like tuples and dereferencing operations (if you use them for finding the bigger and smaller number, it’s entirely optional to use tuples though)
Exer 9. Guessing game
Create a script that will do the following;
- Generate a random integer (whole number), the range is 1 to 1000
- Ask the user for input, ask him to guess a number from 1 to 1000
- Compare your (random) number, from step 1, to the user input
- If the user’s guess is lower that the random number, tell the user, by printing it on the screen “your guess is lower than the number”; otherwise, print “your guess is higher than the number
- On the other hand, if the user has guessed it correctly, then print “you are right, the number is (print the number here)”
Exer 10. Multiples of 3 and 5
If we list all the natural numbers below 10 that are multiples of 3 or 5, we get 3, 5, 6 and 9. The sum of these multiples is 23.
Find the sum of all the multiples of 3 or 5 below 1000.
Hint 1: Answer is 233, 168 → The hint is provided so that you can check your algorithm. It’s the solution we need. (This is Project Euler problem # 1)
Hint 2: You can solve it this way
- Generate a list or range from 1 to 1001 (remember that ranges are exclusive, so if you want to include 1000, you need to terminate the range at 1001)
- Create two lists, call it listA and listB
- Iterate through the range, for each item in it, see if it’s divisible by 3, if it is, add it to listA
- Iterate through the range again, this time, for each item in it, see if it’s divisible by 5, if it is, add it to listB
- listA and listB will have common items in it, because some numbers will be divisible by either 3 or 5
- Combine listA and listB into a single list (listC) but you need to make sure to eliminate the duplicates (try looking into Python sets or using list comprehensions) — you’ll need to do a bit of research in here, visiting stackoverflow isn’t a bad idea
- Now, you can sum all the items in listC
Show the solution using both list comprehension and imperative code (for loops)